前言
在深入分析 Spring 源码前,需要先了解 Spring 框架中的一些核心概念,防止后续看源码的过程中,遇到不会的概念得单独跳出来学习。
主要介绍以下内容:
- 什么是Bean
- BeanDefinition的概念
- BeanFactory的概念
- 比较核心的BeanFactory实现类
- FactoryBean是什么
- FactoryBean的作用
- 什么是BeanPostProcessor
什么是bean
什么是 bean?我们可以来看下 Spring 的官方文档:
In Spring, the objects that form the backbone of your application and that are managed by the Spring IoC container are called beans. A bean is an object that is instantiated, assembled, and otherwise managed by a Spring IoC container. Otherwise, a bean is simply one of many objects in your application. Beans, and the dependencies among them, are reflected in the configuration metadata used by a container.
Spring 是面向 Bean 的编程(Bean Oriented Programming, BOP),Bean 在 Spring 中的作用就像 Object 对 OOP 的意义一样,Spring 中没有 Bean 也就没有 Spring 存在的意义。
Spring 提供了 IoC 容器通过配置文件或者注解的方式来管理对象之间的依赖关系。简而言之,bean 是由 Spring IoC 容器实例化、组装和管理的对象。
BeanDefinition
用来表示 bean 定义,BeanDefinition 中存在很多属性来描述一个 bean 的特点。比如:
- class,表示 bean 的类型
- scope,表示 bean 的作用域,单例或原型等
- lazyInit,表示 bean 是否懒加载
- initMethodName,表示 bean 初始化时要执行的方法
- destoryMethodName,表示 bean 销毁时要执行的方法
- …(等等)
我们可以简单的认为,Spring 在扫描 class 的时候,会根据 class 文件中的注解等信息,给 BeanDefinition 对象赋值,所以,BeanDefinition 是对一个类的描述。那 Spring 在真正去初始化、实例化一个 bean 的时候,直接根据 BeanDefinition 去初始化就可以,比如,在判断这个 bean 是根据类型注入还是根据名字注入的时候,就直接判断 autowireMode 的属性值即可。
编程式定义Bean
在 Spring 中,我们通常会通过以下几种方式来定义 bean:
<bean/>@Bean@Component(@Service,@Controller) 这些,我们可以称之为声明式定义bean。
我们还可以编程式定义 bean,那就是直接通过 BeanDefinition。例如,先定义一个 Bean,但是不添加 @Service 等注解:
| |
然后通过 BeanDefinition 直接定义 ProductService 这个 Bean:
| |
同理,还可以通过 BeanDefinition 设置一个 bean 的其他属性,例如:
| |
和声明式事务、编程式事务类似,通过 <bean/>、@Bean、@Component 等声明式方式所定义的 bean,最终都会被 Spring 解析为对应的 BeanDefinition 对象,并放入 Spring 容器中。
BeanDefinitionReader
接下来我们来介绍几种在 Spring 源码中所提供的 BeanDefinition 读取器(BeanDefinitionReader),这些 BeanDefinitionReader 在我们使用 Spring 时用的少,但在 Spring 源码中用的多,相当于 Spring 源码的基础设施。
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader
可以直接把某个类转换为 BeanDefinition。
我们先定义一个 Bean HelloWorldService:
| |
就可以直接通过 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 把某个类转换为 BeanDefinition :
| |
注意:它能解析的注解是:
- @Conditional
- @Scope
- @Lazy
- @Primary
- @DependsOn
- @Role
- @Description
XmlBeanDefinitionReader
可以用来解析 <bean/> 标签。
例如:
| |
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 是扫描器,但是它的作用和 BeanDefinitionReader 类似,它可以进行扫描,我们可以指定扫描某个路径,让其对扫描到的类进行解析。扫描到的类上如果存在 @Component 注解,那么就会把这个类解析为一个 BeanDefinition,比如:
| |
BeanFactory
BeanFactory 表示 Bean 工厂,BeanFactory 会负责创建 Bean,并且提供获取 Bean 的 API。
Bean 工厂的概念是 Spring 作为 IoC 容器的基础。IoC 则将处理事情的责任从应用程序代码转移到框架。
ApplicationContext 是 BeanFactory 的一种,在 Spirng 源码中是这么定义的:
| |
ApplicationContext 继承了 ListableBeanFactory 和 HierarchicalBeanFactory,而 ListableBeanFactory 和 HierarchicalBeanFactory 都继承至 BeanFactory,所以我们可以认为 ApplicationContext 继承了 BeanFactory 。
ApplicationContext 拥有了 BeanFactory 支持的所有功能,而且比 BeanFactory 更加强大,ApplicationContext 还继承了其他接口,比如 MessageSource 国际化,ApplicationEventPublisher 事件发布,EnvironmentCapable 获取环境变量等等。
在 Spring 源码实现中,当我们 new 一个 ApplicationContext 时,其底层会 new 一个 BeanFactory 出来,当使用 ApplicationContext 某些方法时,比如 getBean() ,底层调用的是 BeanFactory 的 getBean() 方法。
核心的BeanFactory实现类-DefaultListableBeanFactory
在 Spring 源码中,BeanFactory 接口存在一个非常重要的实现类 DefaultListableBeanFactory。所以我们也可以直接使用 DefaultListableBeanFactory ,而不用使用 ApplicationContext 的某个实现类。例如:
| |
DefaultListableBeanFactory 是非常强大的,支持很多功能,我们可以查看下 DefaultListableBeanFactory 的类继承实现结构: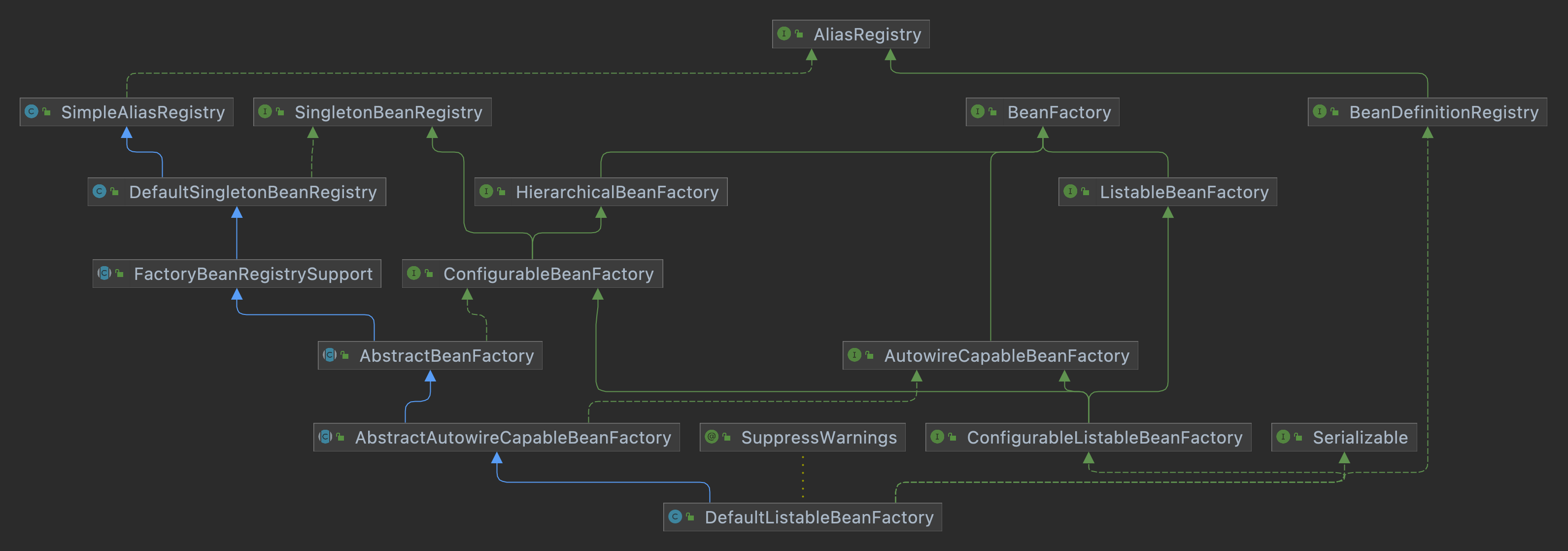
它实现了很多接口,即拥有很多功能:
AliasRegistry支持别名功能,一个名字可以对应多个别名BeanDefinitionRegistry可以注册、保存、移除、获取某个BeanDefinitionBeanfactoryBean工厂,可以根据某个 Bean 的名字、类型、别名获取某个 Bean 对象SingletonBeanRegistry可以直接注册、获取某个单例 BeanSimpleAliasRegistry它是一个类,实现了AliasRegistry接口中所定义的功能,支持别名功能ListableBeanFactory在BeanFactory的基础上,增加了其他功能,可以获取所有BeanDefinition的BeanNames,可以根据某个类型获取对应的 BeanNames,可以根据某个类型获取 类型-对应的Bean 的映射关系HierarchicalBeanFactory在BeanFactory的基础上,添加了获取父BeanFactory的功能DefaultListableBeanFactory它是一个类,实现了SingletonBeanRegistry接口,拥有了直接注册、获取某个单例 Bean 的功能ConfigurableBeanFactory在HierarchicalBeanFactory和SingletonBeanRegistry的基础上,添加了设置父BeanFactory、类加载器(可以指定某个类加载器进行类的加载)、设置 Spring EL表达式解析器(表示该BeanFactory可以解析EL表达式)、设置类型转化服务(表示该BeanFactory可以进行类型转化)、可以添加BeanPostProcessor(表示该BeanFactory支持 Bean 的后置处理器)、可以合并BeanDefinition、可以销毁某个 Bean 等等功能FactoryBeanRegistrySupport支持FactoryBean的功能AutowireCapableBeanFactory直接继承了BeanFactory,在BeanFactory的基础上,支持在创建 Bean 的过程中能对 Bean 进行自动装配AbstractBeanFactory实现了ConfigurableBeanFactory接口,继承了FactoryBeanRegistrySupport,这个BeanFactory功能已经很全面,但是不能自动装配和获取 BeanNames。ConfigurableListableBeanFactory继承了ListableBeanFactory,实现了AutowireCapableBeanFactory、ConfigurableBeanFactoryAbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory继承了AbstractBeanFactory,实现了AutowireCapableBeanFactory,拥有自动装配的功能DefaultListableBeanFactory继承了AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory,实现了ConfigurableListableBeanFactory接口和BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,所以功能很强大
ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext 是个接口,实际上也是一个 BeanFactory ,不过比 BeanFactory 更加强大,比如:
HierarchicalBeanFactory拥有获取父BeanFactory的功能ListableBeanFactory拥有获取 BeanNames 的功能ResourcePatternResolver资源加载器,可以一次性获取多个资源(文件资源等)EnvironmentCapable可以获取运行时环境ApplicationEventPublisher拥有广播时间等功能MessageSource拥有国际化功能
我们可以先来看 ApplicationContext 两个比较重要的实现类:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContextClassPathXmlApplicationContext
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
类继承实现结构: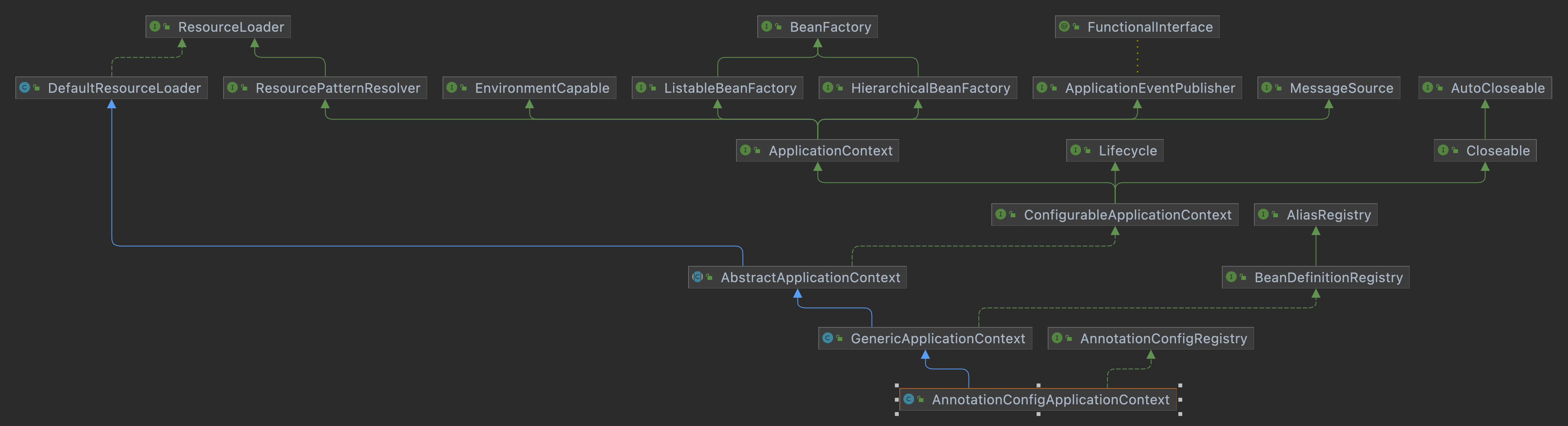
ConfigurableApplicationContext继承了ApplicationContext接口,增加了事件监听器,添加BeanFactoryPostProcessor、设置Environment、获取ConfigurableListableBeanFactory等功能AbstractApplicationContext实现了ConfigurableApplicationContext接口GenericApplicationContext继承了AbstractApplicationContext,实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,拥有所有ApplicationContext的功能,并且可以注册BeanDefinition,注意这个类中有一个属性DefaultListableBeanFactorybeanFactoryAnnotationConfigRegistry可以单独注册某个类为BeanDefinition,可以处理该类上的@Component注解,可以处理@Bean注解,同时可以扫描AnnotationConfigApplicationContext继承了GenericApplicationContext,实现了AnnotationConfigRegistry接口,拥有了以上所有的功能
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
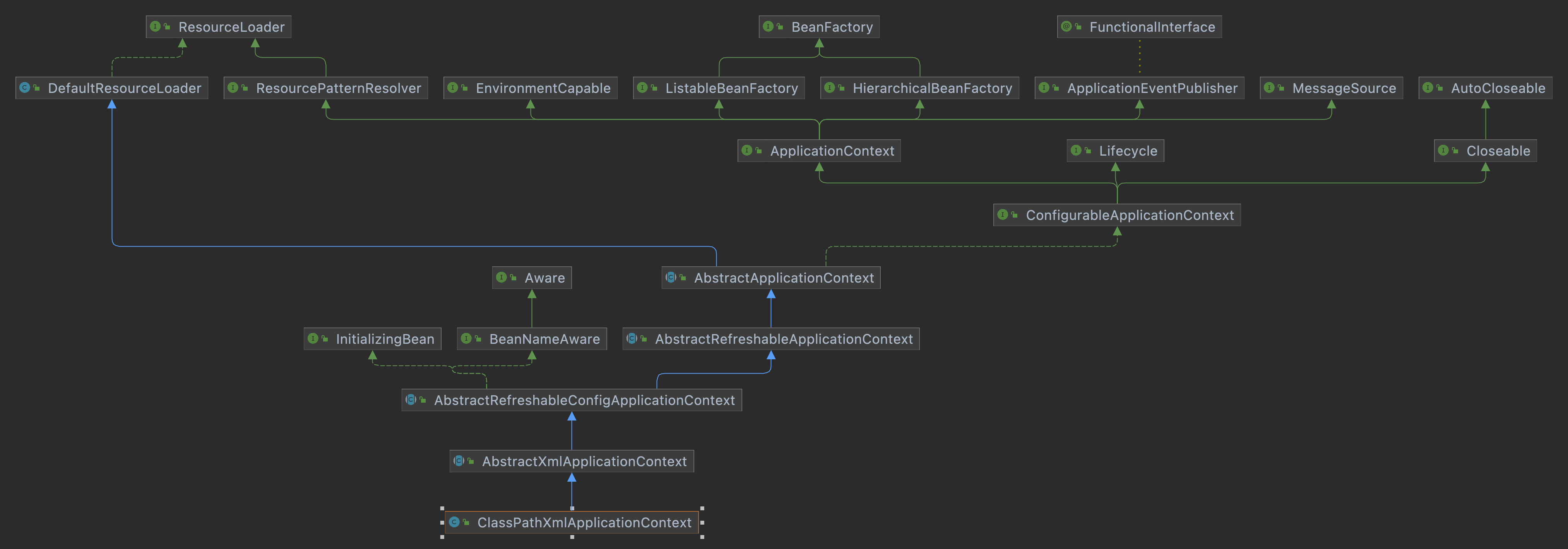
它也是继承了 AbstractApplicationContext,但是相对于 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 而言,功能没有 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 强大,比如不能注册 BeanDefinition
国际化
先定一个 MessageSource:
| |
有了这个 Bean,就可以在任意想要国际化的地方使用该 MessageSource。同时因为 ApplicationContext 拥有国家化的功能,所以也可以这么用:
| |
资源加载
ApplicationContext 还拥有资源加载的功能,可以直接利用 ApplicationContext 获取某个文件的内容:
| |
BeanPostProcessor
表示 Bean 的后置处理器,可以定义一个或多个 BeanPostProcessor 。
一个 BeanPostProcessor 可以在任意一个 Bean 的初始化之前和初始化之后去额外做一些用户自定义的逻辑。我们可以通过判断 beanName 来进行针对性处理(针对某个Bean,或者某部分Bean)。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor
表示 Bean 工厂的后置处理器,其实和 BeanPostProcessor 类似,只不过 BeanPostProcessor 是干涉 Bean 的创建过程,BeanFactoryPostProcessor 是干涉 BeanFactory 的创建过程。
FactoryBean
FactoryBean简单介绍
我们可以通过 BeanPostProcessor 来干涉 Spring 创建 Bean 的过程,但是如果我们想一个 Bean 完完全全由我们来创造,也是可以的,比如通过 FactoryBean 接口。
FactoryBean 翻译过来是工厂Bean,BeanFactory 翻译过来是 Bean 工厂,FactoryBean 是 bean 工厂beanFactory 中的一个 bean,只不过这个 bean 和一般的 bean 不一样,它有着自己的特殊之处,特殊在什么地方呢?这个Bean不是简单的Bean,而是一个能生产或者修饰对象生成的工厂Bean,它的实现与设计模式中的工厂模式和修饰器模式类似。
FactoryBean 接口源码:
| |
FactoryBean 接口很简单,就提供了三个方法 getObject、getObjectType、isSingleton。就是这三个方法却成为了 Spring 中很多功能的基础,搜索整个 Spring 的源码可以找到很多 FactoryBean,除了 Spring 自身提供的以外,在和一些框架进行集成的时候,同样有 FactoryBean 的影子,比如和mybatis集成的时候的 SqlSessionFactoryBean。
FactoryBean示例代码
示例代码:
| |
| |
| |
运行结果:
| |
打印结果很奇怪,通过 myFactoryBean 获得了 Student 对象,通过 &myFactoryBean 获得了 MyFactoryBean 对象。为什么会这样?
这就是
FactoryBean的神奇,通俗点讲FactoryBean是一个工厂bean,它是一种可以生产bean的bean,通过其getObejct方法生产bean。当然不论是FactoryBean还是FactoryBean生产的 bean 都是受 Spring 管理的,不然通过getBean方法是拿不到的。
FactroyBean 的作用是生产一个 bean,这里有一个疑问 Spring 就是用来生产 bean 和管理 bean 的,为什么还要有 FactoryBean?
一般情况下,Spring 通过反射机制利用
<bean>的class属性指定实现类实例化Bean,在某些情况下,实例化Bean过程比较复杂,如果按照传统的方式,则需要在<bean>中提供大量的配置信息。配置方式的灵活性是受限的,这时采用编码的方式可能会得到一个简单的方案。Spring为此提供了一个org.springframework.bean.factory.FactoryBean的工厂类接口,用户可以通过实现该接口定制实例化bean的逻辑。FactoryBean接口对于Spring框架来说占用重要的地位,Spring 自身就提供了70多个FactoryBean 的实现。
FactoryBean 的真正目的是让开发者自己去定义那些复杂的 bean 并交给spring管理,如果bean中要初始化很多变量,而且要进行许多操作,那么使用spring的自动装配是很难完成的,所以 Spring 的开发者把这些工作交给了我们。
ExcludeFilter和IncludeFilter
这两个 Filter 是 Spring 扫描中用来过滤的。ExcludeFilter 是排除过滤器,IncludeFilter 是包含过滤器。
在对 bean 的扫描中会判断 @Component 注解的过滤器。
MetadataReader、ClassMetadata、AnnotationMetadata
在 Spring 中需要去解析类的信息,比如类名、类中的方法、类上的注解,这些都可以称之为类的元数据,所以 Spring 中对类的元数据做了抽象,并提供了一些工具类。
MetadataReader 表示类的元数据读取器,默认实现类为 SimpleMetadataReader 。